Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has redefined how modern organizations operate. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses cut costs, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. Yet, even the most advanced RPA solution can fail without one essential ingredient — proper automation training for employees.
When teams understand how to work alongside digital bots, automation becomes a true partnership between humans and technology. Let’s explore why training is vital, who needs it most, and how to design an effective program that drives lasting RPA success.
Why Employee Training Is the Heart of RPA Success
RPA isn’t about replacing people — it’s about helping them do their jobs smarter. Bots handle rule-based, repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on strategy, creativity, and decision-making. However, this only works when employees understand how automation affects their roles and how to collaborate with the bots effectively.
Without proper training, automation projects risk confusion, errors, and resistance. Trained employees, on the other hand, feel empowered, confident, and capable of managing and optimizing the technology.
Key Benefits of Early Employee Involvement
- Builds Trust and Acceptance: When employees see how bots simplify their workload, they view automation as an ally, not a threat.
- Prevents Costly Mistakes: A well-trained team can identify and fix exceptions before they escalate into operational issues.
- Boosts Efficiency: Employees who understand automation processes keep workflows running smoothly and help sustain high performance.
- The message is simple: RPA success begins with your people.

How Employees Collaborate with Bots
RPA may handle repetitive work, but humans remain in the driver’s seat. Employees perform several critical functions that ensure automation continues to deliver value:
- Exception Handling – Bots can pause when they encounter anomalies. Employees step in, investigate the issue, and resume the process.
- Bot Monitoring – Teams supervise bot performance, ensuring each process runs as expected and remains aligned with business goals.
- Human in the Loop (HITL) – Certain workflows require human input or approval. Trained staff make decisions or verify data when automation reaches a decision point.
- Identifying New Opportunities – Employees familiar with automation can suggest new processes for RPA, driving continuous improvement.
The relationship between humans and bots is collaborative — one ensures efficiency, the other provides oversight and innovation.
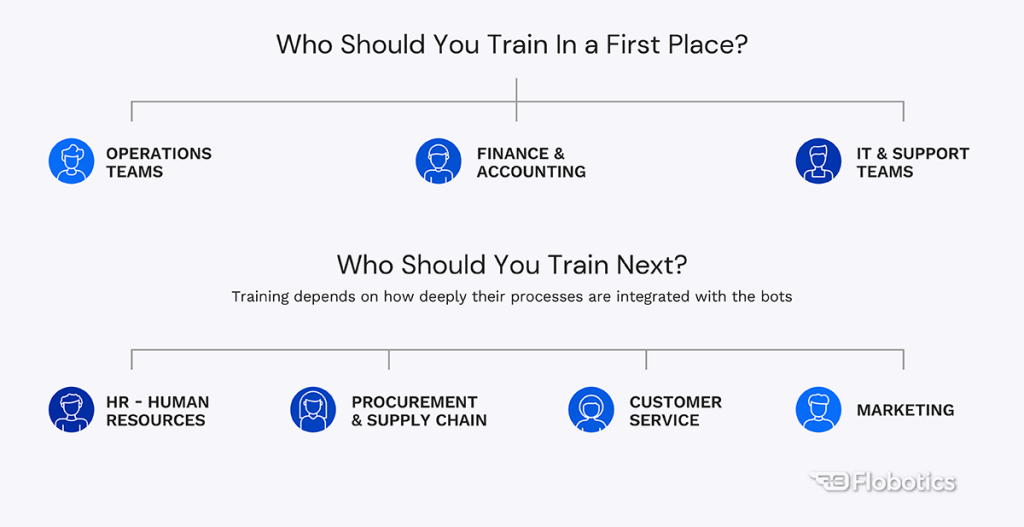
Who Needs Automation Training in Your Organization
Successful RPA implementation depends on training the right people at the right time. Not every department requires the same level of education, but some roles are central to maintaining smooth operations.
Essential Teams for RPA Training
Operations Teams
Most automated workflows begin in operations. These employees interact with bots daily, handle exceptions, and verify task completion. Operations teams must be well-trained to troubleshoot and ensure reliability.
IT and Support Teams
The IT department is the backbone of your automation ecosystem. They oversee bot deployment, platform maintenance, integration, and technical troubleshooting. A deep understanding of RPA tools ensures uptime, security, and scalability.
Optional Departments for RPA Training
- Depending on which processes are automated, other teams may require basic to moderate training:
- Finance and Accounting: Tasks like invoice processing, reconciliation, and reporting are ideal for automation. Teams must learn how to validate data and manage exceptions if these processes are automated.
- Human Resources (HR): Automation simplifies onboarding, payroll, and compliance tracking. HR professionals should understand how to manage automated workflows and review results.
- Customer Service: When bots assist with FAQs or routing tickets, agents need light training to know when to step in and maintain a personal customer touch.
- Procurement and Supply Chain: Automation can accelerate purchase orders, supplier management, and inventory tracking. Trained teams ensure data accuracy and operational flow.
- Marketing: If RPA is used for CRM updates, data collection, or campaign management, marketing professionals should understand automation logic and oversight.
Each department’s training depth depends on the scale and complexity of automation within its workflows. The more interaction with bots, the greater the training need.
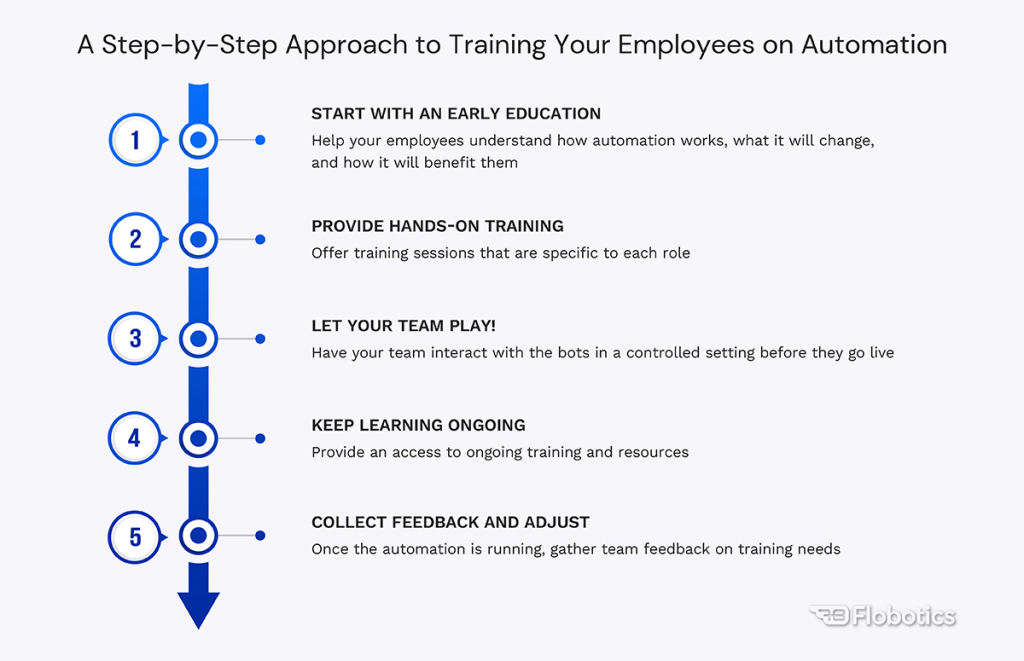
A Practical Guide to Employee Automation Training
An effective automation training program is strategic, structured, and continuous. It ensures that employees feel empowered — not overwhelmed — by technology. Here’s a simple, proven framework:
Begin with Awareness and Education
Before introducing bots, explain the purpose of automation and its benefits. Help employees understand that RPA eliminates tedious work, improves accuracy, and opens new opportunities for growth. Transparency reduces fear and builds excitement.
Deliver Role-Specific Training
- Training should match job responsibilities.
- IT staff learn system maintenance, integrations, and bot lifecycle management.
- Operations teams master exception handling and daily process supervision.
- Managers learn to measure RPA ROI and performance metrics.
- Tailored training ensures everyone knows their part in the automation journey.
Create a Safe Testing Environment
Allow employees to practice interacting with bots in a sandbox or demo system before going live. This reduces anxiety, boosts confidence, and encourages experimentation without disrupting operations.
Maintain Continuous Learning
Automation evolves. Regular refresher sessions and updates keep teams aligned with the latest RPA features and best practices. Create accessible learning materials — video tutorials, FAQs, or short workshops — to keep knowledge fresh.
Collect Feedback and Improve
Once automation is live, gather employee feedback. Are workflows smooth? Do teams face challenges? Continuous feedback helps refine both the automation and the training process, ensuring sustainable improvement.
Best Practices for a Sustainable Automation Culture
Automation training shouldn’t be treated as a one-time project. Building an automation-ready culture empowers every employee to think innovatively and adapt to technological change. Consider these best practices:
- Recognize Champions: Identify and reward employees who embrace automation and help others learn.
- Encourage Cross-Department Collaboration: Allow departments to share insights and successful automation strategies.
- Integrate RPA with Broader Digital Transformation Goals: Align automation with business strategy for greater ROI.
- Use Analytics to Track Training Impact: Monitor performance improvements, reduced error rates, and time savings after training.
When automation becomes part of your company culture, innovation becomes second nature.
The Business Impact of Well-Trained Employees
Training delivers measurable results. Companies that invest in RPA education experience:
- Faster Implementation: Trained teams deploy and scale automation more effectively.
- Reduced Downtime: Fewer operational disruptions thanks to knowledgeable support staff.
- Higher ROI: Automation delivers stronger returns when employees actively optimize processes.
- Improved Morale: Teams that understand technology feel valued, empowered, and future-ready.
Ultimately, trained employees don’t just support automation — they amplify its power.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is a technology that uses software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. It helps businesses save time, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency.
Why is automation training important for RPA success?
Automation training equips employees with the knowledge and confidence to work effectively with bots. It ensures smooth adoption, prevents errors, and helps teams identify new automation opportunities.
How does automation training benefit employees?
Training helps employees understand how bots support their daily tasks, reduces fear of job loss, and empowers them to focus on higher-value work that requires creativity and decision-making.
Which departments need RPA training the most?
Core teams like Operations and IT require extensive RPA training. Other departments such as Finance, HR, Customer Service, and Procurement may need role-specific training depending on automation scope.
What topics should RPA training cover?
A strong training program covers bot operation, exception handling, monitoring, troubleshooting, and identifying new automation opportunities. It should also include hands-on practice sessions.
How long does it take to train employees on automation?
Training duration varies based on the complexity of automation and employee roles. Basic training may take a few days, while advanced technical sessions for IT staff can last several weeks.
What is “Human in the Loop” in RPA?
“Human in the Loop” refers to scenarios where human input or decision-making is required during an automated process. It ensures accuracy and oversight where full automation isn’t possible.
Conclusion
The true secret to a seamless RPA triumph lies not just in powerful technology but in empowered people. Automation training transforms employees into confident collaborators who understand, manage, and enhance the performance of bots. When your workforce embraces automation, efficiency soars, errors drop, and innovation flourishes. By investing in structured and ongoing RPA training, organizations build a future-ready culture that thrives on change and continuous improvement. The result is not only smoother automation adoption but also a stronger, smarter, and more agile business.

